Background
Peripheral T-cell lymphomas, not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS) are a diverse and aggressive type of non-Hodgkin lymphomas with a poor prognosis when treated with conventional chemotherapy. The standard CHOP chemotherapy regimen typically yields an overall response rate (ORR) of 60-80%, a complete response (CR) rate of 30-40%, and long-term survival, measured by 5-yr OS,in the range of 20-30% in non-ALCL (anaplastic large cell lymphoma) subtypes. Azacitidine plus CHOP has achievied a 75% CR in newly diagnosed PTCL, but patients with DNMT3A mutation showed adverse progression-free survival (PFS), indicating that genetic mutations may influence resistance to chemotherapy. Selinexor has shown promising results in refractory lymphoma patients by inhibiting oncogenes, therefore, the efficacy of selinexor combined salvage regimen in refractory PTCL remains great interest.
Method
Refractory PTCL patients were enrolled to be treated with selinexor plus GDP/ICE/Gemox since December 2021 at our center. Selinexor was administered orally (40 mg day 1, 8, 15) plus GDP (gemcitabine 1g/m2*d1, cisplatin 25mg/m2 d1-d3, dexamethasone 40mg d1-d4), ICE (ifosfamide 1.5g/m2*3d, carboplatin (AUC 5) and etoposide 100mg/m2*3d), Gemox (gemcitabine 1g/m2*d1, oxaliplatin 100mg/m2*d1) every 3 weeks as per physician's choice. Objective response rate (ORR) was evaluated every 3 cycles based on Lugano 2014 criteria and Adverse events (AE) were rated according to the NCI CTCAE 5.0.
Results
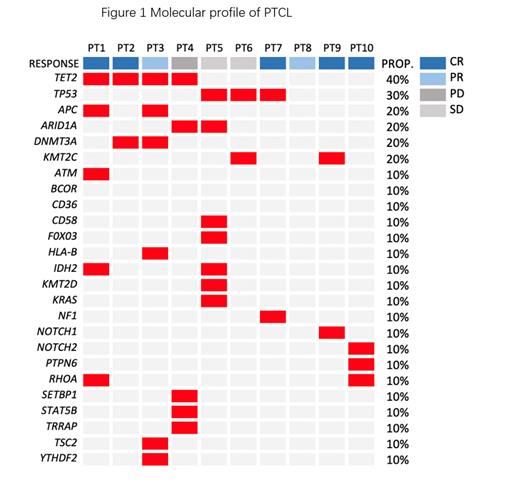
10 patients were treated with selinexor plus salvage regimen in this study and received more than two cycles of the treatment, making them eligible for response evaluation in this poster. The median age of the 10 patients was 65 years (range from 42 to 79), 8 (80%) were male, 9 (90%) had disease stage III-IV at screening, and 60% of all patients had an IPI intermediate to high risk. All of the patients were refractory to the last line of treatment. Among 10 patients, 2 were angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), 3 with PTCL-NOS, 3 with ALK-ALCL, 2 with monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma (MEITL). As shown in Figure 1, 3 patients had TP53 alterations, 2 patients with DNMT3A mutation. Patients received a median of three cycles (range, 2-6) of selinexor 40mg once a week combined with salvage regimen(4 patients received Selinexor-GDP, 3 with selinexor-ICE, 3 with selinexor-Gemox).
The best overall and complete response rates were 70% and 50%, respectively. In terms of MEITL refractory to conventional CHOP treatment, 1 achieved PR but progressed and died after stop treatment for three months due to Covid19 and 1 in CR with selinexor maintenance.
Conclusions
There are limited options for the treatment of refractory PTCL. We identified a dosing schedule of selinexor (40mg qw) with GDP/ICE/Gemox that is efficiency inrefractory PTCL and is worthy of further study on its mechanism of action.
OffLabel Disclosure:
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
The study of selinexor in combination with dexamethasone, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide chemotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell or natural-killer/T-cell lymphoma showed promising results. Out of the 10 evaluable patients, the overall response rate (ORR) was 91%, indicating a significant proportion of patients responding to the treatment. Additionally, the complete response rate (CR) was 82%, showing a substantial number of patients achieving a complete disappearance of the disease. Moreover, the TOUCH study demonstrated encouraging efficacy of selinexor in combination with GEMOX for the treatment of relapsed or refractory PTCL/NKTL. This combination therapy has shown promising results in patients with this type of lymphoma. It is worth noting that selinexor has already obtained approval for the treatment of relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), indicating its potential as a valuable treatment option for patients with this condition. Overall, the results from these studies suggest that selinexor in combination with various chemotherapy regimens holds significant promise for the treatment of relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell and natural-killer/T-cell lymphoma, as well as DLBCL.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal